3326. Count Pairs of Connectable Servers in a Weighted Tree Network
Medium
Array
Tree
Depth-First Search
Description
You are given an unrooted weighted tree with n vertices representing servers numbered from 0 to n - 1, an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional edge between vertices ai and bi of weight weighti. You are also given an integer signalSpeed.
Two servers a and b are connectable through a server c if:
a < b,a != candb != c.- The distance from
ctoais divisible bysignalSpeed. - The distance from
ctobis divisible bysignalSpeed. - The path from
ctoband the path fromctoado not share any edges.
Return an integer array count of length n where count[i] is the number of server pairs that are connectable through the server i.
Example 1:
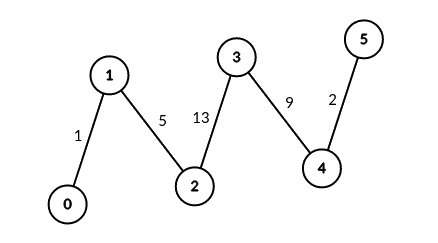
Input: edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,5],[2,3,13],[3,4,9],[4,5,2]], signalSpeed = 1 Output: [0,4,6,6,4,0] Explanation: Since signalSpeed is 1, count[c] is equal to the number of pairs of paths that start at c and do not share any edges. In the case of the given path graph, count[c] is equal to the number of servers to the left of c multiplied by the servers to the right of c.
Example 2:
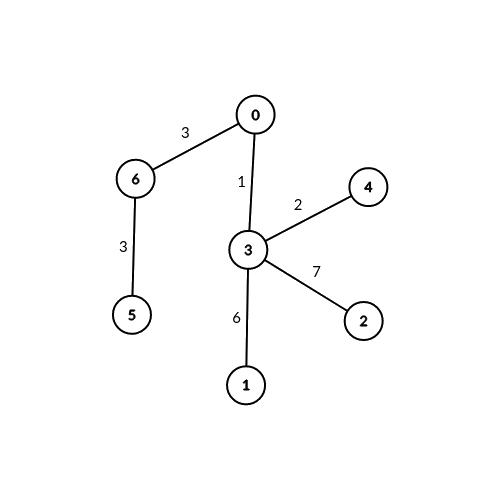
Input: edges = [[0,6,3],[6,5,3],[0,3,1],[3,2,7],[3,1,6],[3,4,2]], signalSpeed = 3 Output: [2,0,0,0,0,0,2] Explanation: Through server 0, there are 2 pairs of connectable servers: (4, 5) and (4, 6). Through server 6, there are 2 pairs of connectable servers: (4, 5) and (0, 5). It can be shown that no two servers are connectable through servers other than 0 and 6.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1000edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 30 <= ai, bi < nedges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti]1 <= weighti <= 1061 <= signalSpeed <= 106- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Hints
Hint 1
Take each node as the root of the tree, run DFS, and save for each node <code>i</code>, the number of nodes in the subtree rooted at <code>i</code> whose distance to the root is divisible by <code>signalSpeed</code>.
Hint 2
If the root has <code>m</code> children named <code>c<sub>1</sub>, c<sub>2</sub>, …, c<sub>m</sub></code> that respectively have <code>num[c<sub>1</sub>], num[c<sub>2</sub>], …, num[c<sub>m</sub>]</code> nodes in their subtrees whose distance is divisible by signalSpeed. Then, there are <code>((S - num[c<sub>i</sub>]) * num[c<sub>i</sub>]) / 2</code>that are connectable through the root that we have fixed, where <code>S</code> is the sum of <code>num[c<sub>i</sub>]</code>.
Similar Questions
Statistics
Acceptance
55.7%
Submissions
29,272
Accepted
16,310