2627. Difference Between Maximum and Minimum Price Sum
Description
There exists an undirected and initially unrooted tree with n nodes indexed from 0 to n - 1. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Each node has an associated price. You are given an integer array price, where price[i] is the price of the ith node.
The price sum of a given path is the sum of the prices of all nodes lying on that path.
The tree can be rooted at any node root of your choice. The incurred cost after choosing root is the difference between the maximum and minimum price sum amongst all paths starting at root.
Return the maximum possible cost amongst all possible root choices.
Example 1:
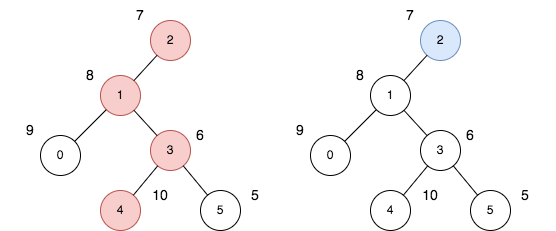
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4],[3,5]], price = [9,8,7,6,10,5] Output: 24 Explanation: The diagram above denotes the tree after rooting it at node 2. The first part (colored in red) shows the path with the maximum price sum. The second part (colored in blue) shows the path with the minimum price sum. - The first path contains nodes [2,1,3,4]: the prices are [7,8,6,10], and the sum of the prices is 31. - The second path contains the node [2] with the price [7]. The difference between the maximum and minimum price sum is 24. It can be proved that 24 is the maximum cost.
Example 2:
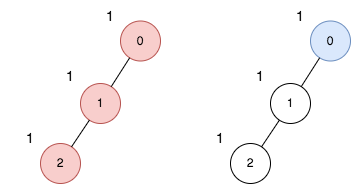
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2]], price = [1,1,1] Output: 2 Explanation: The diagram above denotes the tree after rooting it at node 0. The first part (colored in red) shows the path with the maximum price sum. The second part (colored in blue) shows the path with the minimum price sum. - The first path contains nodes [0,1,2]: the prices are [1,1,1], and the sum of the prices is 3. - The second path contains node [0] with a price [1]. The difference between the maximum and minimum price sum is 2. It can be proved that 2 is the maximum cost.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 10 <= ai, bi <= n - 1edgesrepresents a valid tree.price.length == n1 <= price[i] <= 105