3218. Find Number of Coins to Place in Tree Nodes
Hard
Dynamic Programming
Tree
Depth-First Search
Sorting
Heap (Priority Queue)
Description
You are given an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array cost of length n, where cost[i] is the cost assigned to the ith node.
You need to place some coins on every node of the tree. The number of coins to be placed at node i can be calculated as:
- If size of the subtree of node
iis less than3, place1coin. - Otherwise, place an amount of coins equal to the maximum product of cost values assigned to
3distinct nodes in the subtree of nodei. If this product is negative, place0coins.
Return an array coin of size n such that coin[i] is the number of coins placed at node i.
Example 1:
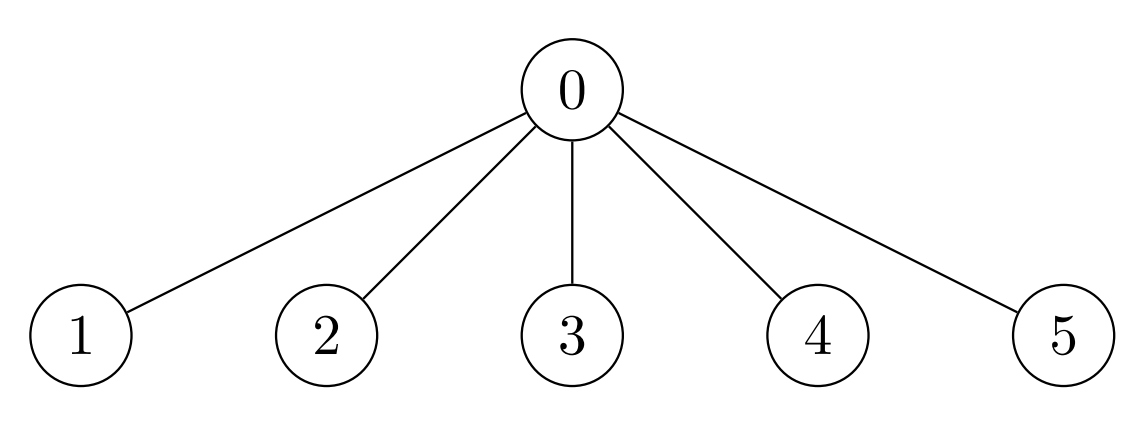
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5]], cost = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: [120,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: For node 0 place 6 * 5 * 4 = 120 coins. All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 2:
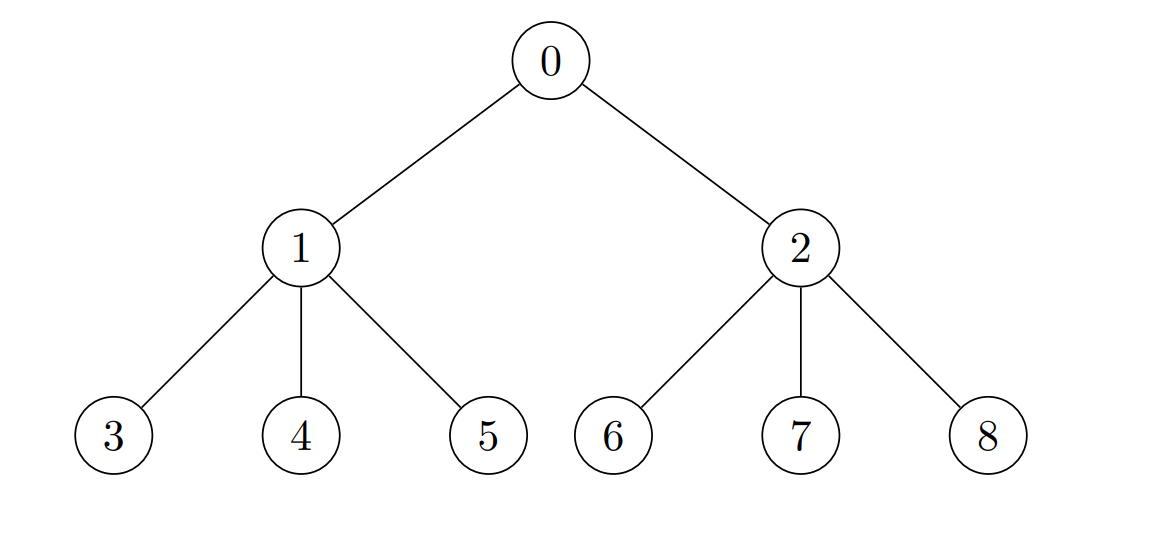
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,7],[2,8]], cost = [1,4,2,3,5,7,8,-4,2] Output: [280,140,32,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The coins placed on each node are: - Place 8 * 7 * 5 = 280 coins on node 0. - Place 7 * 5 * 4 = 140 coins on node 1. - Place 8 * 2 * 2 = 32 coins on node 2. - All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 3:
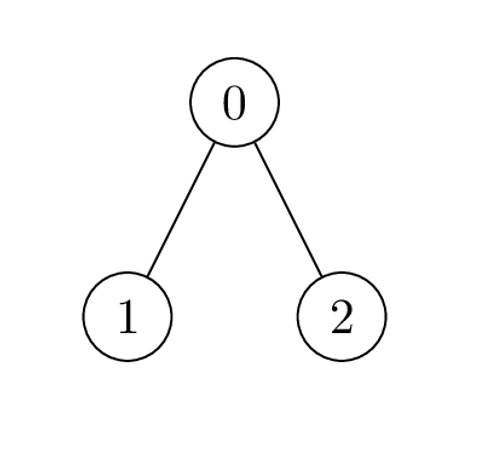
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], cost = [1,2,-2] Output: [0,1,1] Explanation: Node 1 and 2 are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them. For node 0 the only possible product of cost is 2 * 1 * -2 = -4. Hence place 0 coins on node 0.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < ncost.length == n1 <= |cost[i]| <= 104- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Hints
Hint 1
Use DFS on the whole tree, for each subtree, save the largest three positive costs and the smallest three non-positive costs. This can be done by using two Heaps with the size of at most three.
Hint 2
You need to store at most six values at each subtree.
Hint 3
If there are more than three values in total, we can sort them. Let’s call the resultant array <code>A</code>, the maximum product of three is <code>max(A[0] * A[1] * A[n - 1], A[n - 1] * A[n - 2] * A[n - 3])</code>. Don’t forget to set the result to <code>0</code> if the value is negative.
Hint 4
If there are less than three values for a subtree, set its result to <code>1</code>.
Similar Questions
Statistics
Acceptance
37.4%
Submissions
29,939
Accepted
11,183