2558. Minimum Number of Operations to Sort a Binary Tree by Level
Medium
Tree
Breadth-First Search
Binary Tree
Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values.
In one operation, you can choose any two nodes at the same level and swap their values.
Return the minimum number of operations needed to make the values at each level sorted in a strictly increasing order.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
Example 1:
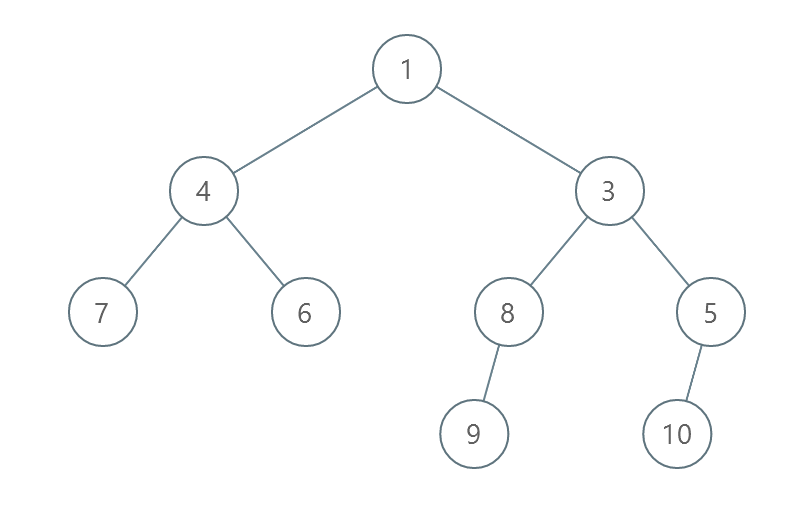
Input: root = [1,4,3,7,6,8,5,null,null,null,null,9,null,10] Output: 3 Explanation: - Swap 4 and 3. The 2nd level becomes [3,4]. - Swap 7 and 5. The 3rd level becomes [5,6,8,7]. - Swap 8 and 7. The 3rd level becomes [5,6,7,8]. We used 3 operations so return 3. It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 2:
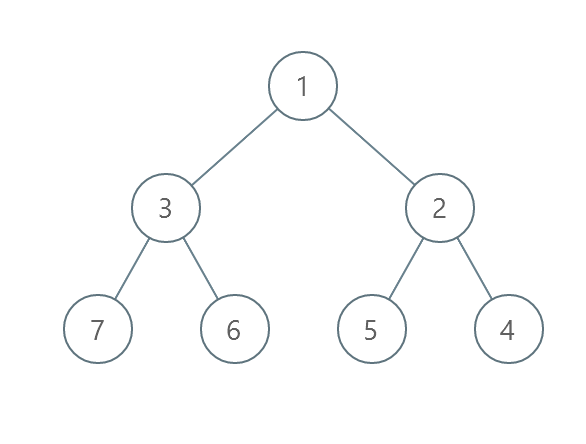
Input: root = [1,3,2,7,6,5,4] Output: 3 Explanation: - Swap 3 and 2. The 2nd level becomes [2,3]. - Swap 7 and 4. The 3rd level becomes [4,6,5,7]. - Swap 6 and 5. The 3rd level becomes [4,5,6,7]. We used 3 operations so return 3. It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 3:
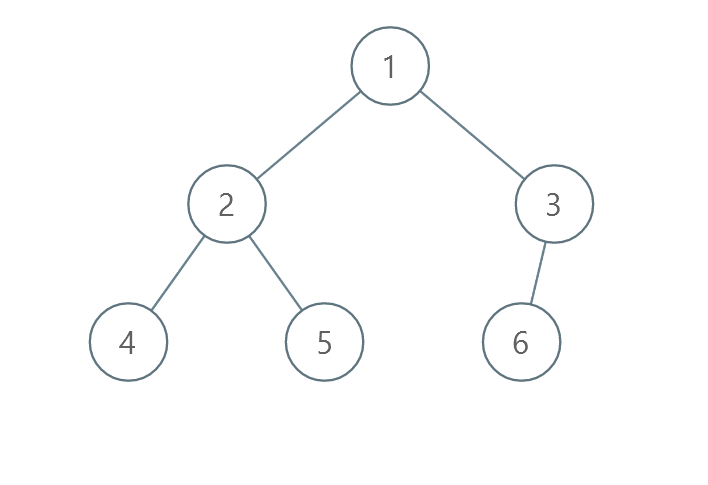
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 0 Explanation: Each level is already sorted in increasing order so return 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- All the values of the tree are unique.
Hints
Hint 1
We can group the values level by level and solve each group independently.
Hint 2
Do BFS to group the value level by level.
Hint 3
Find the minimum number of swaps to sort the array of each level.
Hint 4
While iterating over the array, check the current element, and if not in the correct index, replace that element with the index of the element which should have come.
Similar Questions
Statistics
Acceptance
74.2%
Submissions
153,145
Accepted
113,685